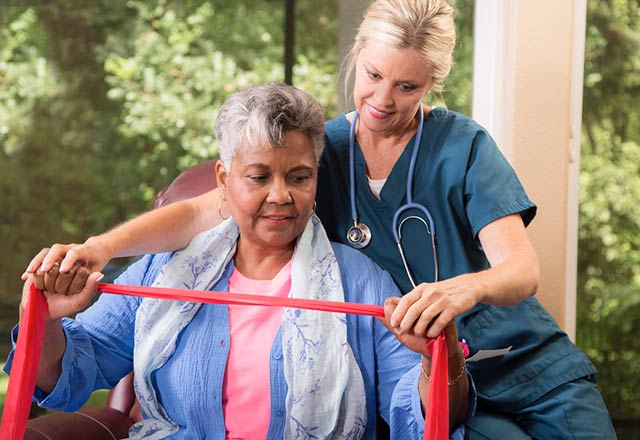
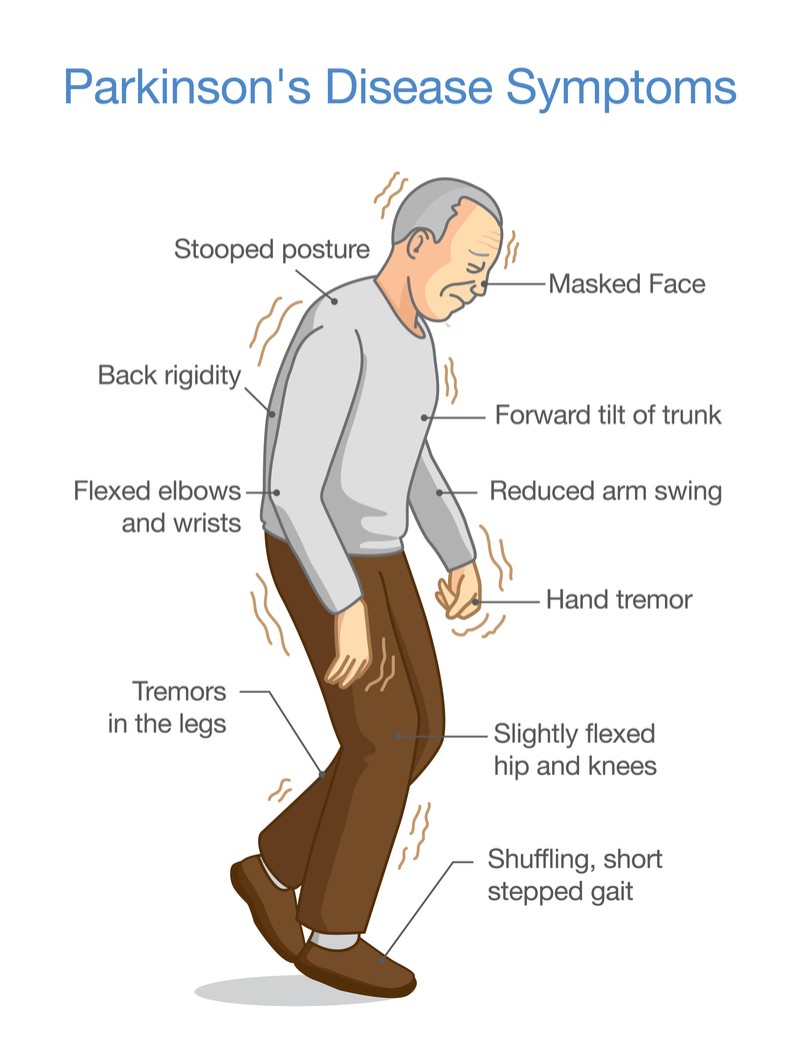
Only randomised controlled trials were included in this review. These were studies where a group of participants were given one physiotherapy intervention and were compared with another group who received a different physiotherapy intervention. The participants were assigned to a group in a random fashion to reduce the potential for bias.
A total of 43 randomised trials involving 1673 participants (average trial size of just 39 participants) were identified as suitable for this review. The trials assessed various physiotherapy interventions, so they were grouped according to the type of intervention being used (general physiotherapy, exercise, treadmill training, cueing, dance or martial arts). However, despite this grouping, the physiotherapy interventions delivered and the outcomes assessed varied so much that the results of the individual trials could not be combined.
This review highlights that a wide range of different physiotherapy techniques have been tested to treat PD. Considering the small number of participants, the wide variety of physiotherapy interventions and the outcomes assessed, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of one approach of physiotherapy intervention over another for the treatment of PD.